Inflation in the economy is a term that describes the rate of increase in prices for goods and services and the decline in the purchasing power of the currency. To put it another way, it refers to the degree to which the quantity of a particular product purchased in a single currency varies.
Different schools of economists evaluate inflation both positively and negatively. However, as practice shows, inflation is an inevitable event, experienced every year even by states with strong economies. The main factor is stability. The main goal of the state is to pursue an economic, fiscal and monetary policy that ensures a stable inflation rate. This makes it much easier to assess the risks and predict the events.
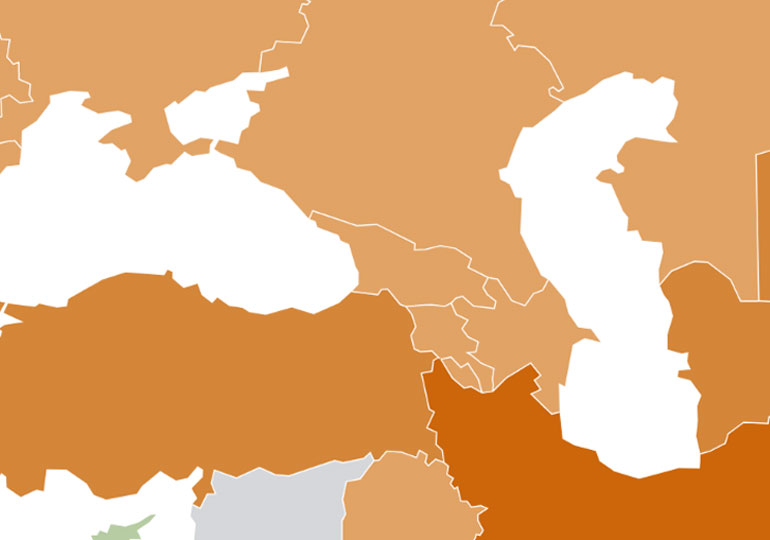
One of the most authoritative financial institutions in the world, the International Monetary Fund publishes a monthly World Economic Outlook document that combines multiple criteria. A combination of GDP, inflation and other macroeconomic factors are included in the document. According to the IMF’s World Economic Outlook for October, the inflation rate in Georgia stands at 9.3%.
This figure is one of the highest in the region. Inflation in Russia is 5.9% over the same period, which is quite a decent figure in light of the recent COVID outbreak. Inflation is quite low in our southern neighbor Azerbaijan. Inflation there stands at 4.4%. In Armenia, the same figure is equal to 6.9%.
In turn, the situation is dire in yet another neighboring country, Turkey. The inflation rate here is 17%, which could have negative consequences for the Turkish economy. The country’s national currency, Lira, has depreciated significantly and is at a record low of the decades. Ukraine has a similar situation as Georgia, with the inflation rate at 9.5%.
According to the International Monetary Fund, the inflation rate in Georgia will stabilize over the next year and will reach 5.4%, which is an acceptable rate for the normal development of the country’s economy.