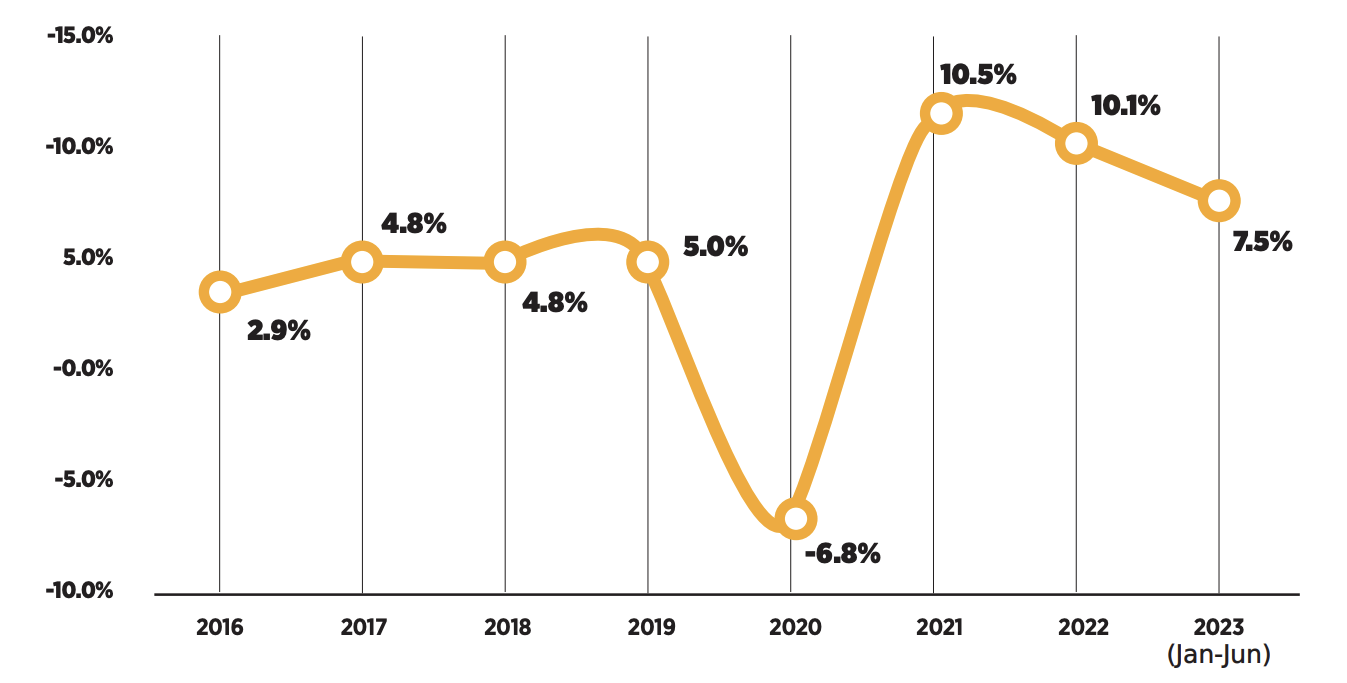
The Georgian economy grew by 10.1% in 2022. In 2023, however, the economic growth rate started to decrease. Year-on-year growth was 7.7% in the first quarter of 2023 and 7.5% in the second quarter. As a result, the growth rate in the first half of the year (January to June) was 7.6%. The final figures for the third quarter have not been released yet, but preliminary figures show that the economy grew by 5.5% in July and 5.8% in August. This means the overall growth figure for the first eight months of the year (January to August) was 7%.
Economic growth implies an increase in Georgia’s real gross domestic product (GDP), which shows the percentage growth in the volume of goods and services produced in the country. Real GDP growth does not include an increase driven by inflation.
Given that the main economic figures for the first half of 2023 are available, we can delve into what drove Georgia’s 7.6% economic growth.
The Economic Growth of Georgia
Let us start by looking at which sectors registered the highest growth from January to June 2023. The IT and communications sector led the way with 31.3% growth, followed by construction (19%), education (16.4%) and trade (14.3%). The most significant decline in growth was recorded in the agricultural sector (-5.4%), followed by processing (-4.6%) and mining (-4.5%).
Apart from the growth rate, it is also important to note the size of the relevant industry. The larger the sector, the faster the country’s growth rate. In the first half of 2023, trade and vehicle repairs contributed the most to the 7.6% total growth of the Georgian economy (2.2%). In 2022, this sector grew by 6%, while its share of the total growth was 0.9%. The significant year-on-year increase is linked to the fourfold increase in vehicle re-exports, which boosted the volume of trade and vehicle repair services.
The second-largest share in the growth of the economy (1.4%) is held by the construction sector, which grew by 19% on the back of increased demand for residential housing and state-funded infrastructure projects.
The fastest-growing sector – IT and communications with 31.3% – contributed 1.4% to the total growth. In 2022, this sector grew by 50% and contributed 1.7% to the total growth, driven by increased demand for computer services. The rapid growth of this industry started in 2021 when it grew by 30%. The arrival of Russian, Belarussian and Ukrainian migrants conditioned subsequent growth acceleration. According to the GeoStat Business Register, around 1,200 companies were operating in the field of computer services in Georgia in 2022, including up to 600 foreign private firms. 470 of these enterprises were registered in Georgia after the outbreak of the full-scale war in Ukraine on the 24th of February 2022, and Russian nationals own 90% of them. In total, 40% of IT companies operating in Georgia are Russian-owned. According to data from the National Bank of Georgia, the total amount received for providing computer and information services to residents of foreign countries by companies registered in Georgia in the first half of 2023 amounted to $430 million, representing a threefold year-on-year increase. This was the main driver behind the 31.3% growth in the sector.
The Georgian Economy by Sector, January to June 2023
Economic Activity | Million GEL | Growth Rate | Share in Economic Growth, % |
| Trade, vehicle repair | 4678 | 14.3% | 2.2 |
| Construction | 2234 | 19.0% | 1.4 |
| IT and communications | 1607 | 31.3% | 1.4 |
| Education | 1701 | 16.4% | 0.9 |
| Public governance | 2303 | 10.8% | 0.8 |
| Arts, entertainment and leisure | 1402 | 9.6% | 0.5 |
| Hotels and restaurants | 1075 | 11.8% | 0.4 |
| Financial activities | 1620 | 7.3% | 0.4 |
| Transport and warehousing | 1852 | 5.3% | 0.3 |
| Professional and technical activities | 676 | 9.3% | 0.2 |
| Real estate | 3507 | 1.2% | 0.1 |
| Mining | 396 | -4.5% | -0.1 |
| Electricity, gas and air supply | 974 | -4.1% | -0.2 |
| Healthcare | 1271 | -6.3% | -0.3 |
| Agriculture | 2056 | -5.4% | -0.4 |
| Processing | 2839 | -4.6% | -0.6 |
| Other | 560 | 18% | 0.6 |
Source: Geostat
Trade, construction and IT accounted for 5% of the 7.6% growth in the first half of 2023, which indicates that the war in Ukraine and the subsequent influx of around 100,000 migrants to Georgia continues to have a significant impact on economic growth in 2023, similar to last year.
Education, public governance, and entertainment are other sectors that have significantly contributed to economic growth. Their total share in the growth was 2.1%.
If we break down Georgia’s GDP according to expenses, we can see that the growth of the economy from January to June 2023 was influenced by an increase in service exports and capital formation (investment). Service exports increased by 42% in tourism, IT and transport. Capital formation increased by 11.6%. Economic growth, therefore, was not driven by domestic consumption, which increased by 4.2%; it was outpaced by the import of goods and services (4.4%).
It is interesting to look at the factors that are not visible from GDP figures but significantly contributed to the increase in production (supply) and the consumption of goods and services (demand). In this regard, three key elements stood out in the first half of 2023:
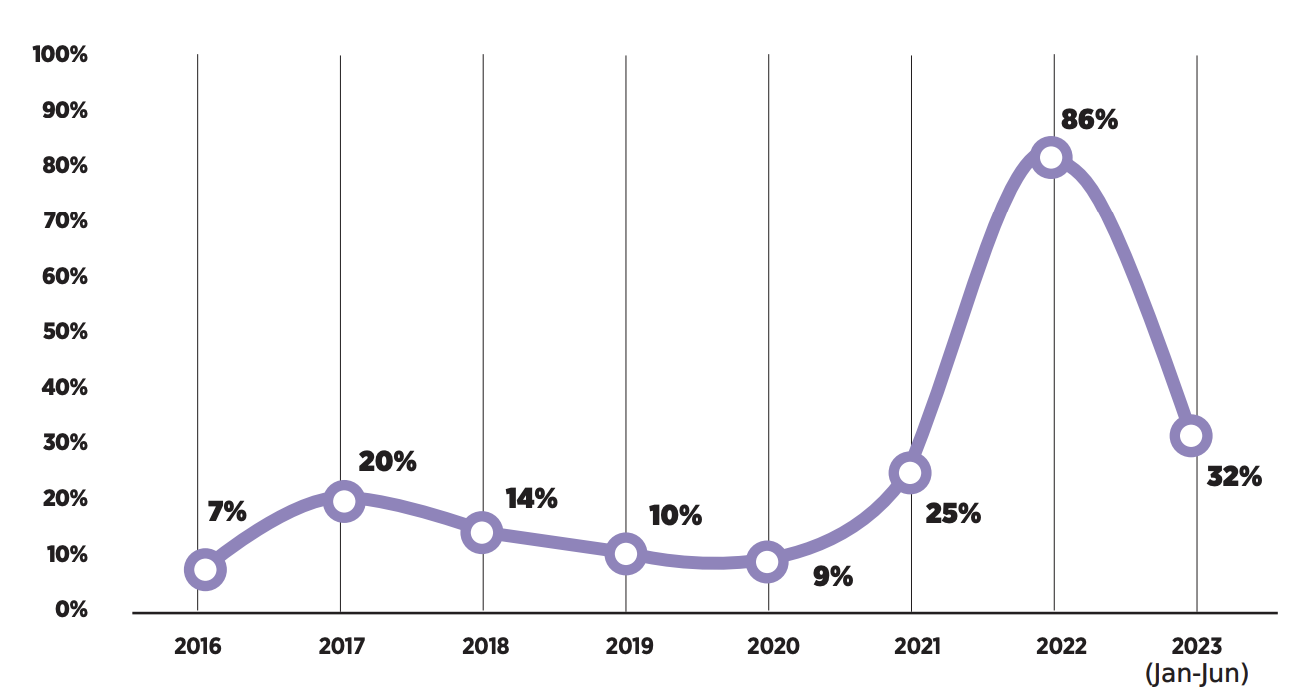
- The volume of remittances to Georgia, an essential source of income for the country’s population, increased by 32% year-on-year to $2.4 billion. Remittances from Russia increased by 50% to $1.1 billion.
- The number of visitors to Georgia increased by 76% year-on-year to 2.9 million. The highest increase was in the number of Russian visitors – an increase of 330,000 to 578,000. The volume of money spent by visitors in Georgia increased by 58% to $1.8 billion. Russian visitors spent $482 million, 2.2 times more than in the same period last year.
- The volume of foreign direct investment in Georgia, which raises GDP growth potential, increased by 11% to $1.1 billion. The processing sector accounted for the highest volume of FDI ($262 million), followed by finance ($261 million), energy ($202 million) and trade ($125 million).
Remittance Growth Rate
The Georgian government’s economic growth forecast for 2023 is 6.5%. Although the growth rate fell below 6% in July, the 7.6% figure achieved in the first half of the year makes 6.5% a realistic target. According to IMF data, only 12 countries worldwide are expected to reach more than 6.5% economic growth in 2023.
The main reason for the slowdown in economic growth is the reduction in remittances and the export of goods. The volume of remittances increased by an average of 100% from January to April 2023 but began to decrease from May and fell by an average of 17% each month up to and including September. This is mainly due to a reduction in remittances from Russia, which decreased by 46% in August and by 66% in September. Nevertheless, the figures are up to 60% higher compared to the August-September 2021 period before the outbreak of the war in Ukraine.
The export of goods increased by an average of 21% per month in the first half of 2023 and decreased by 1% in July. They then increased by 5% in August and 1% in September. The virtual halt in the overall growth of exports was caused by a significant decrease in the export of ferroalloys (77%), copper alloys (56%) and fertilizers (41%). Together, the exports in these three groups decreased by $240 million.
Despite the slowdown in economic growth this year, remittances from Russia and changes caused by the war in Ukraine still contributed significantly to growth. Similar trends are taking place in neighboring Armenia, which is expected to grow 7% this year. This would place it fifth in the world.